To ensure its contributions to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are effective, globally relevant, and scalable, ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ actively pursued international partnerships in 2024 focused on the review and adoption of best practices (SDG 17).
To ensure its contributions to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are effective, globally relevant, and scalable, ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ actively pursued international partnerships in 2024 focused on the review and adoption of best practices (SDG 17). This strategy involved benchmarking academic curricula, integrating advanced clinical methodologies, and participating in policy dialogues informed by comparative international research. By deliberately engaging with leading universities and specialized institutions worldwide, the College strategically imports high-standard operating models that directly strengthen national capacity across critical areas like health, education, environmental sustainability, and governance.
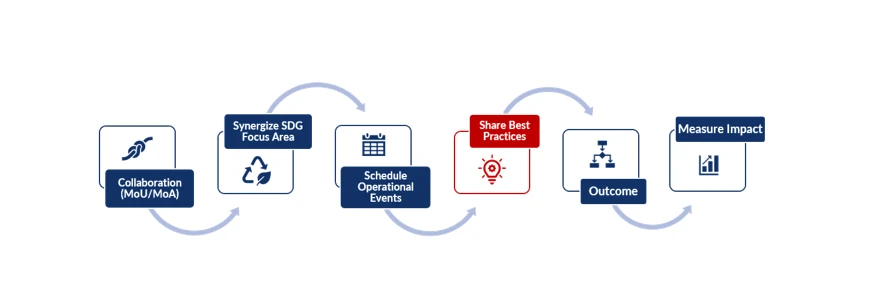
ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ's approach to international knowledge exchange is governed by a systematic, six-phase Best Practice Adoption Model. This structured process ensures that collaborations are not isolated events but are strategically aligned to yield measurable improvements in both academic delivery and national SDG contribution.
Collaboration (Formal MoU/MoA): The process begins with securing formal agreements (MoU/MoA) with a reputable international institution. This formalizes the relationship and establishes a secure, long-term framework for mutual exchange and quality assurance.
Synergize SDG Focus Area: The partnership's operational activities are explicitly synergized and aligned with specific, critical SDGs (e.g., connecting a health partner to SDG 3, or a science partner to SDG 14).
Schedule Operational Events: Practical implementation is initiated through scheduled operational events (e.g., joint faculty exchanges, public lectures, collaborative research projects, or joint training sessions) to facilitate direct knowledge transfer.
Share Best Practices: The core activity involves the direct and documented sharing of best practices (e.g., curriculum standards, clinical simulation protocols, governance models, or research methodologies) from the international partner to ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ.
Outcome: These shared practices are then reviewed, adapted, and integrated, leading to a tangible outcome (e.g., a revised and benchmarked curriculum, a new training module, or informed policy input used nationally).
Measure Impact: Finally, the resultant impact on quality, student competency, or national policy is measured and documented to complete the cycle of continuous improvement.

The following initiatives detail the mechanisms through which international best practices were exchanged and integrated into ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ's operations and the Maldivian context, categorized by the primary SDG focus area.
ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ has established a critical strategic academic partnership with Chitkara University, India, formalized through a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), which is specifically designed to strengthen expertise in subjects vital to the Maldivian environment. This MoU functions as a robust Best Practice Sharing Mechanism, enabling ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ to rigorously benchmark its curriculum design, research methodologies, and institutional policies in key SDG Focus Areas (SDG 4, 14, and 15) against an established international institution. For the Maldives, a Small Island Developing State (SIDS), this collaboration is paramount, as Chitkara University provides high-value, structured frameworks for the rigorous integration of advanced environmental science and sustainability modules into the College's curriculum. This direct input is instrumental in helping ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ rapidly build national expertise in Marine Conservation (SDG 14) and Coastal Ecosystem Management (SDG 15), ensuring its training is effective and relevant through the adoption of proven global research methods. Moreover, this collaboration explicitly enables both institutions to engage in mutual learning regarding curriculum delivery and resource optimization.

To uphold the highest levels of educational delivery, the partnership directly addresses SDG 4 (Quality Education) by facilitating the peer review of quality assurance protocols and faculty development programs, ensuring that all educational content adheres to international academic standards. The Chitkara partnership is a core component of a wider strategic commitment to SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals), with ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ maintaining many other similar academic MoUs with international institutions, including Al Ahliyya Amman University (Jordan), Amity University (India), and SR University (India), to continuously enhance its educational offerings and research capacity.
Best Practice Sharing Mechanism: The MoU facilitates the sharing of University Practices in SDG Focus Areas, allowing ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ to benchmark its curriculum design, research methodologies, and institutional policies against an established international university.
SDG Focus Areas: SDG 4 (Quality Education), SDG 14 (Life Below Water), and SDG 15 (Life on Land).
The Faculty of Health Sciences prioritized SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) by partnering with global health institutions, including the Apollo Simulation Center for Advanced Clinical Training and TACT Academy for Clinical Training Private Limited (TACT), to dramatically improve the practical competency of its graduates. These formal collaborations provide access to international clinical training models and High-Fidelity Simulation (HFS) protocols—the global gold standard for preparing health professionals. ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ reviews and adopts these HFS standards by training VC faculty in scenario-based learning, debriefing techniques, and using simulation equipment to replicate critical patient care scenarios. This strategic shift from purely theoretical instruction to a competency-based practical assessment model ensures that the College's nurses and health workers graduate with measurable, high-quality skills necessary for safe and effective national health service delivery, fostering a shared best practice in maintaining clinical realism and evaluating practical skills.
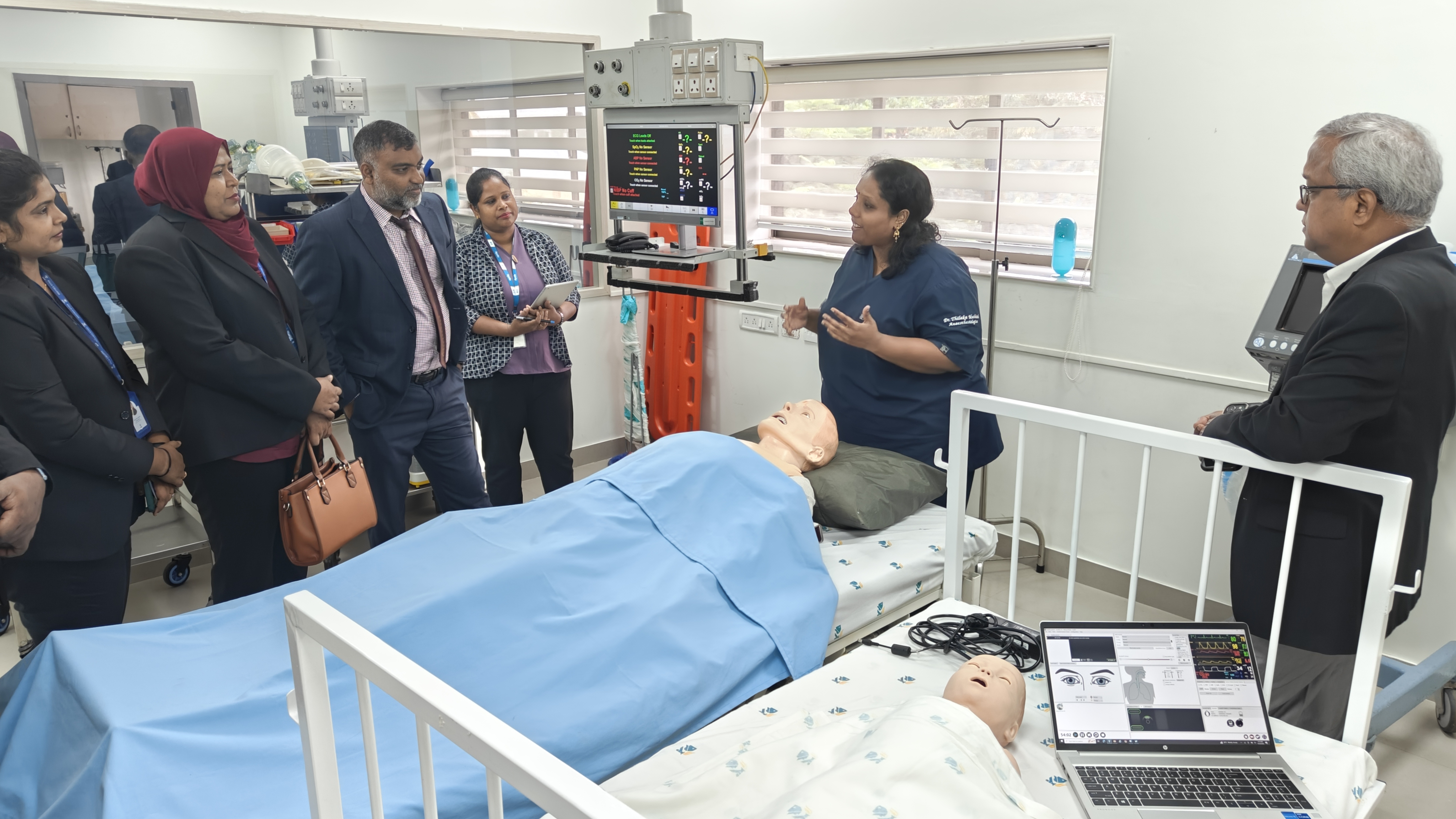 Best Practice Sharing Mechanism: These partnerships provide access to international clinical training models and simulation protocols—the current global gold standard for preparing health professionals.
Best Practice Sharing Mechanism: These partnerships provide access to international clinical training models and simulation protocols—the current global gold standard for preparing health professionals.
SDG Focus Area: SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 4 (Quality Education)
ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ strategically utilizes international MoUs to align its professional offerings with global requirements, demonstrating a commitment to SDG 4 (Quality Education), SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), and SDG 17 (Partnerships). The core of this effort is the formal MoU with INCEIF (International Centre for Education in Islamic Finance), Malaysia, which serves as the primary Best Practice Sharing Mechanism through the development of joint educational programmes and faculty exchange. This partnership is crucial for integrating international best practices in Islamic Finance, ensuring that ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ graduates receive a curriculum that meets international professional standards and prepares them to compete globally. The shared practices specifically emphasize the pedagogy for complex financial instruments and compliance standards, promoting the adoption of ethical and sustainable financial models that contribute to a resilient national economy (SDG 8).

Best Practice Sharing Mechanism: The collaboration involves developing joint educational programmes and faculty exchange to integrate international best practices in Islamic Finance.
SDG Focus Areas: SDG 4 (Quality Education), SDG 17 (Partnerships), and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ strategically implemented a Scheduled Operational Event to directly import cutting-edge research and practice on workplace mental health, demonstrating its commitment to SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth). The College hosted a public lecture by Prof. Carla Semedo of the University of Évora, Portugal, under the SSAPI project, functioning as the Best Practice Sharing Mechanism through the Direct Knowledge Transfer of European Occupational Health Psychology Frameworks. This focused intervention provided a comparative approach to identifying and mitigating Psychosocial Risks in the workplace—a key area of modern occupational safety best practice. This direct knowledge transfer introduced cutting-edge research and practice on workplace mental health and Psychosocial Risks, directly advancing SDG 3 (Good Health) and further reinforcing the College’s commitment to providing a productive, healthy, and secure work environment in alignment with global standards for well-being. The immediate benefit is that the knowledge shared directly informs the College's internal well-being policies, while also providing a vital research basis for local academics to develop interventions. This initiative ensures the Maldivian context is aligned with robust international standards, thereby enhancing the health and productivity of the workforce across the nation.

Best Practice Sharing Mechanism: Direct knowledge transfer of European Occupational Health Psychology frameworks.
SDG Focus Areas: SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being) and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ successfully utilized a high-profile collaboration with an international civil society body to benchmark its research influence and policy contribution methods, directly supporting SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions) and SDG 17 (Partnerships). This institutional advancement was centered on the research study, 'Unveiling Public Trust in the Maldivian Media,' commissioned by the International Federation of Journalists (IFJ). This partnership established a Best Practice Sharing Mechanism through the Adoption of Internationally Recognized Research Methodology for Governance and Policy Analysis. Crucially, the IFJ's involvement ensured that the methodology used to measure sensitive indicators like public trust, media perception, and journalistic independence adhered to rigorous global standards. The public dissemination of these findings via the "Noosveringe Salla" dialogue further established a best practice model for Evidence-Based Policy Advocacy in the Maldives, effectively demonstrating how an academic institution can collaborate with international organizations to foster transparency, rigor in research, and ultimately contribute to stronger national institutions.
Best Practice Sharing Mechanism: Adoption of internationally recognized research methodology for governance and policy analysis.
SDG Focus Areas: SDG 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions) and SDG 17 (Partnerships).
ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ’s sustained and targeted use of international MoUs, collaborations, and expert knowledge transfer sessions highlights a sophisticated institutional strategy: leveraging SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) as the core Best Practice Sharing Mechanism to drive measurable improvements across the Maldivian context. The initiatives span critical areas of national importance, demonstrating systematic impact from clinical skills (SDG 3, 4) to national governance (SDG 16). The adoption of High-Fidelity Simulation (HFS) protocols in Health Sciences, the rigorous benchmarking of Islamic Finance education via INCEIF (SDG 8), and the direct knowledge transfer of European Occupational Health Psychology frameworks (SDG 3) all represent deliberate moves to embed global gold standards into local practice. Furthermore, partnerships, such as the one with Chitkara University, provide essential frameworks for Environmental Education, Marine Conservation, and Coastal Ecosystem Management (SDG 14, 15), rapidly building expertise vital for a Small Island Developing State (SIDS). By ensuring research methodologies adhere to internationally recognized standards (IFJ/SDG 16) and translating these findings into Evidence-Based Policy Advocacy, ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ successfully moves beyond mere theoretical instruction. Ultimately, this strategic commitment ensures the institution’s educational offerings and policy contributions are not only relevant but are also globally certified, cementing ÃÜÌÒÊÓƵ's role as a central driver of high-quality education and resilient national capacity development.